Measles Information
If you think that your child may have the measles, please let our office know when scheduling the appointment. This will allow us to make safe arrangements (for your child as well as other children in the office) for your child to be evaluated.
What is measles?
Measles is a serious respiratory disease (in the lungs and breathing tubes) that causes a rash and fever. It is very contagious. In rare cases, it can be deadly.
What are the symptoms of measles?
The symptoms of measles generally appear about seven to 14 days after a person is infected.
Measles typically begins with:
- high fever,
- cough,
- runny nose
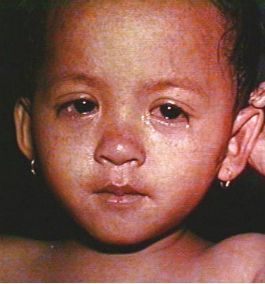
- red, watery eyes
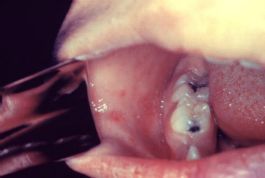
Two or three days after symptoms begin, small red, irregularly-shaped spots with blue-white centers (Koplik spots) may appear inside the mouth.
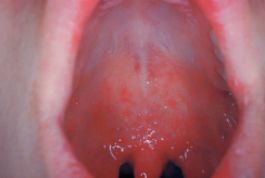
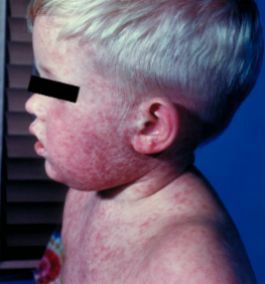
Three to five days after symptoms begin, a rash breaks out. It usually begins as flat red spots that appear on the face at the hairline and spread downward to the neck, trunk, arms, legs, and feet. Small raised bumps may also appear on top of the flat red spots. The spots may become joined together as they spread from the head to the rest of the body. When the rash appears, a person’s fever may spike to more than 104° Fahrenheit.
After a few days, the fever subsides and the rash fades.
Is measles a serious disease?
Measles can be dangerous, especially for babies and young children. From 2001-2013, 28% of children younger than 5 years old who had measles had to be treated in the hospital.
For some children, measles can lead to:
- Pneumonia (a serious lung infection)
- Lifelong brain damage
- Deafness
- Death
How does measles spread?
Measles is a highly contagious virus that lives in the nose and throat mucus of an infected person. It can spread to others through coughing and sneezing. Also, measles virus can live for up to two hours on a surface or in an airspace where the infected person coughed or sneezed. If other people breathe the contaminated air or touch the infected surface, then touch their eyes, noses, or mouths, they can become infected. Measles is so contagious that if one person has it, 90% of the people close to that person who are not immune will also become infected.
Infected people can spread measles to others from four days before to four days after the rash appears.
Measles is a disease of humans; measles virus is not spread by any other animal species.
What are the complications of measles?
Measles can be a serious in all age groups. However, children younger than 5 years of age and adults older than 20 years of age are more likely to suffer from measles complications.
Common Complications:
Common measles complications include ear infections and diarrhea.
- Ear infections occur in about one out of every 10 children with measles and can result in permanent hearing loss.
- Diarrhea is reported in less than one out of 10 people with measles.
Severe Complications:
Some people may suffer from severe complications, such as pneumonia (infection of the lungs) and encephalitis (swelling of the brain). They may need to be hospitalized and could die.
- As many as one out of every 20 children with measles gets pneumonia, the most common cause of death from measles in young children.
- About one child out of every 1,000 who get measles will develop encephalitis (swelling of the brain) that can lead to convulsions and can leave the child deaf or mentally retarded.
- For every 1,000 children who get measles, one or two will die from it.
Measles may cause pregnant woman to give birth prematurely, or have a low-birth-weight baby.
What is the treatment for measles?
There is no treatment for measles. Medical care is supportive to help relieve symptoms.
How can measles be prevented?
Measles is a vaccine preventable disease. The best way to protect against measles is to get the measles-mumps-rubella shot (called the MMR shot). Doctors recommend that all children get the MMR shot.
Where can I get more information?
- CDC – Measles Vaccination Information
- CDC – About Measles
- CDC - Measles Cases and Outbreaks
- New Jersey Department of Health – Measles Information
- MedlinePlus – Measles Information